
How to Measure BMI for Adults, Children & Teens
BMI or body mass index is a measurement used to determine body size. The calculation is simply a combination of a person’s height in relation to their weight. Typically a person’s BMI is taken to determine whether their weight is correct for their height.
BMI is also used to determine whether an individual is at a healthy weight, underweight, or overweight. If a person’s BMI does not fall within a healthy range, they may be more susceptible to health risks.
Those who are underweight may suffer from:
- Osteoporosis
- Anemia
- Malnutrition
Those who are overweight may suffer from:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular problems
- High blood pressure
Keep in mind that BMI is not determined by directly measuring body fat. BMI also does not take into account the muscle mass in adults, sex, ethnicity, or age. Instead, BMI relies upon standard weight status categories that are used by doctors to identify potential health issues as well as keep track of weight status across populations.
How to calculate BMI for adults
Metric
As we already know, you can determine an individual’s BMI by measuring their body weight and height. Let’s take a look at the formulate needed to calculate BMI in metric units:
Metric
As we already know, you can determine an individual’s BMI by measuring their body weight and height. Let’s take a look at the formulate needed to calculate BMI in metric units:
BMI = kg/m2
If you were to calculate the BMI for an adult you would divide their weight in kilograms (kg) by the square of their height in meters (m2). For the segment of the world that uses centimeters (cm) to measure height, simply divide the height of an individual in cm by 100 to ascertain height in meters.
Imperial
You can also determine BMI by using the imperial system. Let’s take a look at the formula for this method:
BMI = lbs x 703/in2
When using this method of measurement to determine BMI in an adult, multiply the weight of the individual in question in pounds (lbs) by 703. Take that number and divide by their height in inches, squared (in2).
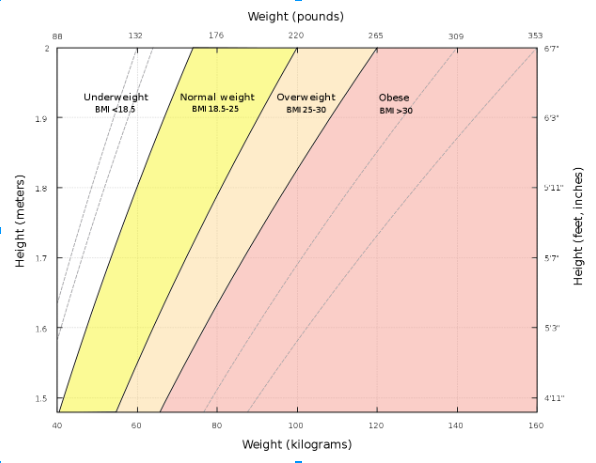
Using equations to determine BMI is just one way to go about it. You can make your task exponentially easier by using a chart (courtesy of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute) or calculator.
Understanding the BMI chart
To interpret a BMI chart, simply find your height in inches on the appropriate side of the chart. Now you can trace across to ascertain your body weight (measured in pounds). Once you’ve done this look along the top of the chart where you can determine the range of your BMI (normal, overweight, or obese).
Gaining a better understanding of the results
Here’s a breakdown of the standard weight status categories typical for the BMI ranges for adults.
| BMI | Weight Status |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Healthy |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 and above | Obese |
A BMI below 18.5 is an indication that you are underweight. Consult your doctor for advice, but more than likely you will have to gain more weight until you reach healthy levels.
A BMI of 18.5 – 24.9 is an indication that you are at a healthy weight range in relation to your height as an adult. Work to maintain this weight as you will significantly reduce your risks of developing health complications later on down the line.
A BMI of 30 and above is an indication that you are obese. Seek advice from your doctor, but you will need to lose weight or you will be more susceptible to severe health complications.
BMI in children and teenagers
An important distinction must be made before proceeding any further. The range of BMI values for adults have nothing to do with sex or age. However, this is not the case for children and teens.
During adolescence physical development is often different for boys and girls. Each age may bring differing amounts of body fat for both sexes. Thus, both sex and age are considered when measuring BMI for children and teens.
Children and teens aren’t categorized via their healthy weight ranges by health professionals for several reasons. For one, the fact that they’re constantly growing means their weight will likely change on a regular basis. Their BMI would always be in constant flux because they’re not just growing heavier, but also taller. Also, boys and girls often change at different rates.
When determining a child or teen’s BMI, doctors will measure their weight and height just as they do with adults. Next, they’ll use a sex/age specific BMI chart to learn their BMI number. This number will be used to determine whether the child or teen falls into a healthy range.
Determining BMI for children and teens
While you could determine the BMI of children and teenagers with a variety of equations, you can save yourself the trouble by using a BMI calculator. You can then use a chart to help you determine the results of your calculation.
First, use the calculator. Now, refer to the below charts to determine whether or not a child or teen’s weight is in a healthy range for their age.
Click here to find a chart for girls age 2 – 20 years. Click here to find a chart for boys 2 – 20 years old.
Interpreting the results
Use these categories to help you interpret the results of your calculations:
| Weight status category | Percentile range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Below the 5th percentile |
| Healthy weight | 5th percentile to less than the 85th percentile |
| Overweight | 85th to less than the 95th percentile |
| Obesity | Equal to or greater than the 95th percentile |
How do doctors and medical professionals use BMI?
While BMI is incredibly helpful, it can only be used for screening purposes to identify potential health complications in children and adults. It doesn’t have the accuracy to be used as a diagnostic tool.
Doctors rarely rely upon just BMI before deciding on a corrective course of action for their patients to take. If a patient’s BMI falls outside of a healthy range, doctors may also consider the following:
- Exploring family history to identify possible cardiovascular diseases and other such health issues.
- Taking measurements of skinfold thickness as this can indicate the amount of fat contained within the body of a patient.
- Recommend other health screenings in relation to your situation.
- Evaluate factors such as physical activity and diet.
The many benefits of maintaining a healthy weight
There are numerous benefits to maintaining a healthy weight range. These include:
- Improved sleep
- Reduced risk of developing dangerous health conditions
- Less stress on the joints and muscles thus reducing the possibility of pain
- Less burden on the circulatory system and heart
- More energy and physical ability to participate in a range of activities
The many health risks of being overweight
Being overweight or obese can have overtly negative consequences for your body. These include:
- Increased possibility of developing diabetes amongst other debilitating heart issues
- Increased load on the heart
- Lowered levels of lipoprotein (good cholesterol)
- Increases chances of raising blood pressure to higher levels
Being overweight greatly increases your chances of experiencing/developing a variety of conditions that include:
- Stroke
- High blood pressure or hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes
- Dyslipidemia
- Coronary heart disease
- Gallbladder disease
- Asthma
- Osteoarthritis
- Increased psychological stress
- Low self-esteem
- Respiratory issues
- Sleep apnea
- Increased chance of developing certain types of cancers such as breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
Other measurements to consider
BMI has proven to be an incredibly effective tool. With that being said, however, it can’t be used to determine whether or not a person’s body is made up of fat or muscle. Identifying the actual amount of fat in your body (as opposed to muscle) is important because it can help your doctor to give a more accurate diagnosis.
For example, those who have visceral fat around their gut are more at risk of developing high blood pressure and cardiovascular diseases.
Other measurements exist to help provide a complete picture of a patient’s health. These include:
- Waist-to-height ratio
- Waist-hip ratio
- Body composition (a measure of lean body mass and body fat)
The above measurements are used to determine the amount of fat an individual has and where it’s located in their body. These additional measurements in combination with BMI are an incredibly effective way to more accurately determine the potential health risks an individual may face in relation to their weight.
Featured Image Credit:U.S. Air Force photo illustration by Airman 1st Class Destinee Sweeney
In Post Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons